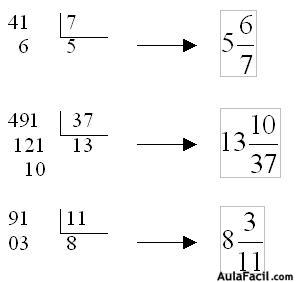
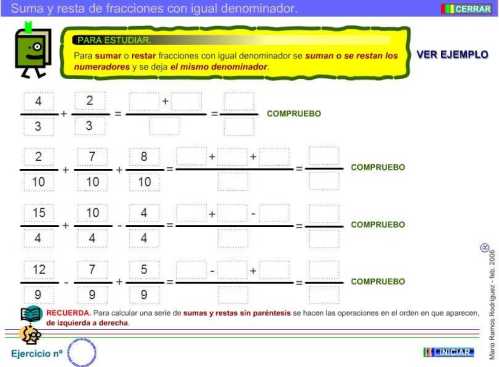
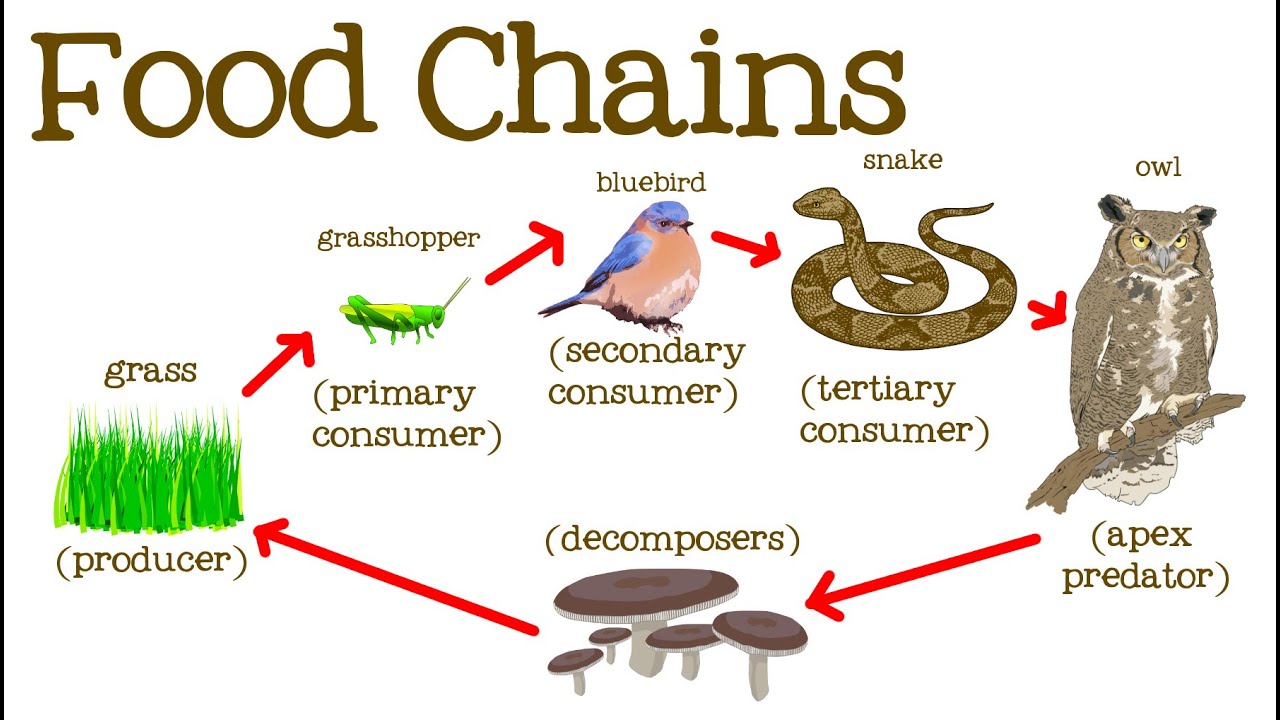
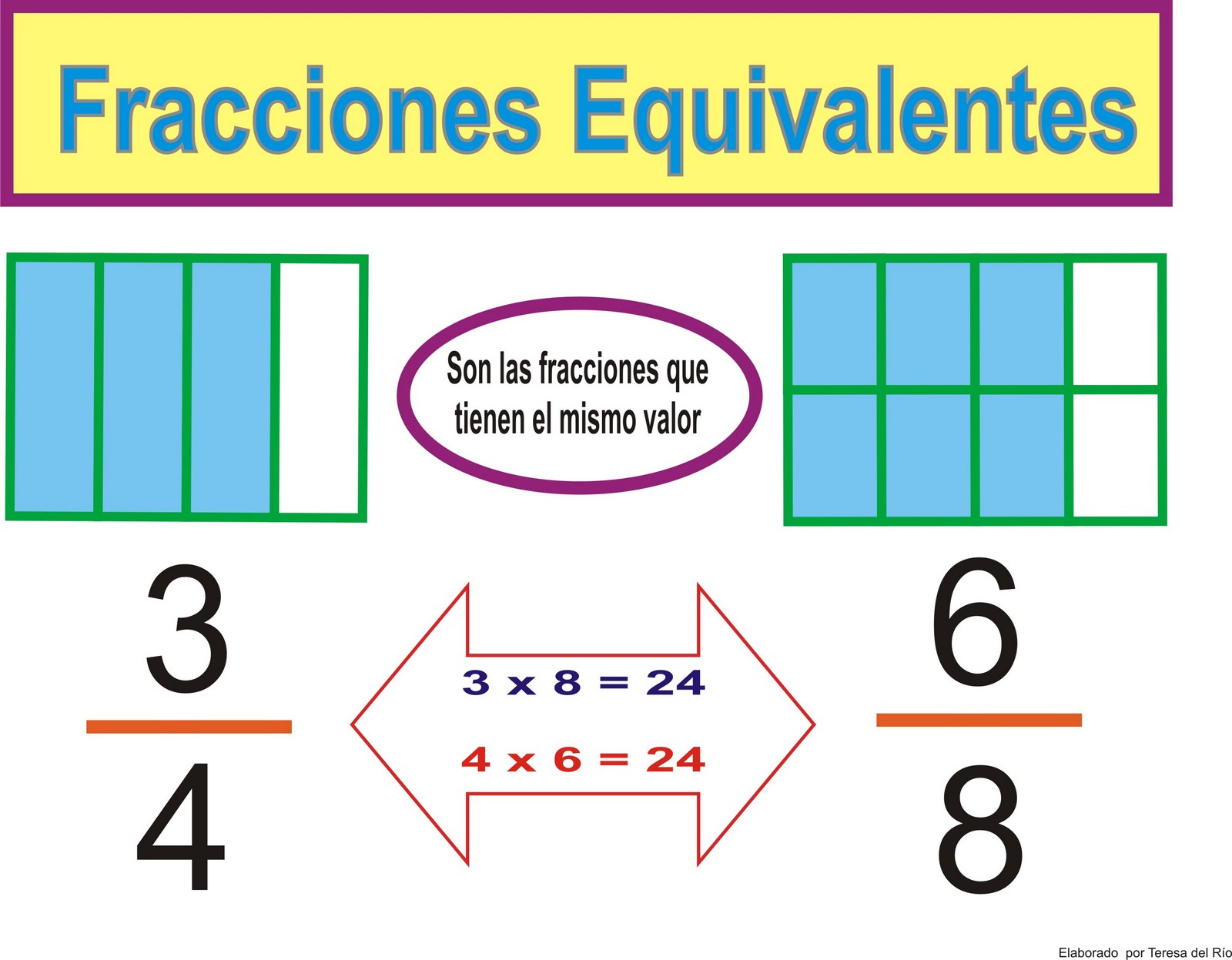
There are many types of ecosystems. To classify them, we examine their physical environment.
Pond ecosystems are small areasof water and their surrounding land.
The water, the soil or sand at the bottom of the pond and the banks of the pond are non-living things.
Aquatic plants such as water lilies, and animals such as ducks, turtles, pond skaters and dragonflies are found in this ecosystem.
Woodland ecosystems can be flat or hilly. They sometimes have mountains and valleys.
There are non-living things such as soil and rocks, rivers or streams and also dead leaves and branches.
Among the living things, there are plants such as trees and shrubs. Many animals live here: snakes, squirrels, birds and insects such as beetles and ants.
 |
| Picture from BBC |
Coast ecosystems have non-living things, such as the land and water along the coast, beaches, cliffs, dunes and rock pools.
Many different living things are found there: plants such as seaweed and dune grasses, and animals such as seagulls, fish and starfish.
Prairie ecosystems are large, flat areas.
The non-living things include soil and often rivers or lakes.
There are a variety of living things. Grasses and shrubs grow there, so prairies are sometimes called grasslands or savannahs.Zebras, rabbitsand owls, and insects such as grasshoppers and ants, are commonly found there.
City ecosystems can be flat or hilly with rivers or lakes, or on the coast. Buildings and roads are some of the non-living things in cities, but there are a variety of living things too.
Cities often have parks and gardens. Grasses, trees and bushes can all be found in most cities. Cities are home to many types of birds, such as mice, lizards, insects and sometimes foxes, can also be found.
_(21009123989).jpg)



,_Lincolnshire_Road_Transport_Museum,_23_July_2005.jpg)





,_Madrid,_Spain.jpg)